<h1>最小费用最大流</h1>
<h2>定义</h2>
我想你一定学会了最大流算法。
模板题链接
我们发现在同一个网络中,可能会有多个总流量相同的最大流 $f$,我们可以在计算流量的基础上,给网络中的弧增加一个单位流量的费用(简称费用),在确保流量最大的前提下总费用最小,这样的最大流叫做最小费用最大流。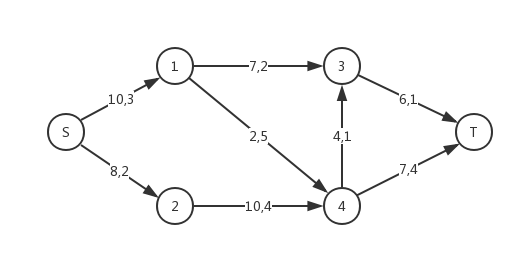
在上面这个网络中,弧上用逗号分隔的两个数分别为弧的容量和单位流量费用。例如,一条流量为 $2$、经过 $S \to 1 \to 4 \to T$ 的流的费用是 $(3+5+4)*2 = 24$。
<h2>做法</h2>
首先每条边多了一个属性“费用”,对于反向边怎么加呢?
我们可以这样:
inline void add(int u,int v,int cap,int cost){
node[u].first = New(&node[u],&node[v],cap,cost);
node[v].first = New(&node[v],&node[u],0,-cost);
node[u].first->rev = node[v].first;
node[v].first->rev = node[u].first;
}
// 看不懂指针的朋友:这里就是反向边的消费是正向边的相反数的意思,
接下来我们按照以下流程来实现:
- 网络初始流量为 $0$
- 在当前的残量网络上求出从 $S$ 到 $T$ 的最短增广路,以每条弧的单位费用为边权。如果不存在则算法结束
- 统计答案,更改流量,重复步骤 $2$
在绝大多数情况下我们使用 SPFA 算法来求解第 $2$ 步。
<h2>代码</h2>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define Re register
#define LL long long
#define U unsigned
#define FOR(i,a,b) for(Re int i = a;i <= b;++i)
#define ROF(i,a,b) for(Re int i = a;i >= b;--i)
#define SFOR(i,a,b,c) for(Re int i = a;i <= b;i+=c)
#define SROF(i,a,b,c) for(Re int i = a;i >= b;i-=c)
#define CLR(i,a) memset(i,a,sizeof(i))
#define BR printf("--------------------n")
#define DEBUG(x) std::cerr << #x << '=' << x << std::endl
const int MAXN = 5000+5;
const int MAXM = 50000+5;
inline char nc(){
#define SIZE 100000
static char buf[SIZE],p1 = buf+SIZE,pend = buf+SIZE;
if(p1 == pend){
p1 = buf;pend = buf+fread(buf,1,SIZE,stdin);
if(p1 == pend) return -1;
}
return *p1++;
}
inline void read(int &x){
x = 0;int flag = 1;
char ch = nc();
while(!isdigit(ch)){
if(ch == '-') flag = -1;
ch = nc();
}
while(isdigit(ch)){
x = (x<<1) + (x<<3) + (ch^'0');
ch = nc();
}
x *= flag;
}
struct Node{
struct Edge first,pre;
int dist,h;bool vis;
}node[MAXN];
struct Edge{
Node s,t;
Edge next,rev;
int flow,cap,cost;
}pool[(MAXM<<1)+3],*frog = pool;
Edge New(Node s,Node *t,int cap,int cost){
Edge *ret = ++frog;
*ret = (Edge){s,t,s->first,NULL,0,cap,cost};
return ret;
}
inline void add(int u,int v,int cap,int cost){
node[u].first = New(&node[u],&node[v],cap,cost);
node[v].first = New(&node[v],&node[u],0,-cost);
node[u].first->rev = node[v].first;
node[v].first->rev = node[u].first;
}
#define P std::pair<int,Node *>
#define MP std::make_pair
int N,M,S,T;
int maxFlow,minCost;
bool spfa(Node s,Node t){
FOR(i,1,N) node[i].vis = false,node[i].dist = INT_MAX,node[i].pre = NULL;
s->vis = true;s->dist = 0;
std::queue<Node *> q;q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()){
Node *v = q.front();q.pop();
v->vis = false;
for(Edge *e = v->first;e;e = e->next){
if(e->flow < e->cap){
if(e->t->dist > v->dist + e->cost){
e->t->dist = v->dist + e->cost;
e->t->pre = e;
if(!e->t->vis) q.push(e->t),e->t->vis = true;
}
}
}
}
return t->pre != NULL;
}
inline void work(){
while(spfa(&node[S],&node[T])){
int flow = INT_MAX;
for(Node *v = &node[T];v != &node[S];v = v->pre->s){
flow = std::min(flow,v->pre->cap-v->pre->flow);
}
maxFlow += flow;
for(Node *v = &node[T];v != &node[S];v = v->pre->s){
v->pre->flow += flow;
v->pre->rev->flow -= flow;
minCost += v->pre->cost * flow;
}
}
}
int main(){
//freopen("./LG/testdata.in","r",stdin);
read(N);read(M);read(S);read(T);
// DEBUG(N);
while(M--){
int u,v,cap,cost;
read(u);read(v);read(cap);read(cost);
add(u,v,cap,cost);
}
work();
printf("%d %dn",maxFlow,minCost);
return 0;
}
<h1>模型扩展</h1>
<h2>贴纸与玩偶</h2>

其中 $m \leq 100,n \leq 50$。
这个题目就是费用流经典模型了:有两种不同的属性的物品,需要找出两个不同的属性的物品进行配对并规定配对对答案的贡献。并且每种物品数量有限,要求答案最大或最小。
对于上述题目来说:源点连向每个贴纸一条流量为 $a_i$,费用为 $0$ 的弧,每个玩偶连向汇点一条流量为 $b_i$,费用为 $0$ 的弧,每个贴纸连向每个玩偶流量为 $\text{INF}$,费用为 $h_{i,j}$ 的弧,按需跑最小/大费用最大流即可。
<h3>代码</h3>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define Re register
#define LL long long
#define U unsigned
#define FOR(i,a,b) for(Re int i = a;i <= b;++i)
#define ROF(i,a,b) for(Re int i = a;i >= b;--i)
#define SFOR(i,a,b,c) for(Re int i = a;i <= b;i+=c)
#define SROF(i,a,b,c) for(Re int i = a;i >= b;i-=c)
#define CLR(i,a) memset(i,a,sizeof(i))
#define BR printf("--------------------n")
#define DEBUG(x) std::cerr << #x << '=' << x << std::endl
const int MAXN = 1000+5;
const int MAXM = 10000+5;
struct Node{
struct Edge first,pre;
int dist;bool inq;
}node[MAXN];
struct Edge{
Node s,t;
Edge next,rev;
int cap,flow,cost;
}pool[MAXM<<1],*frog = pool;
Edge New(Node s,Node *t,int cap,int cost){
Edge *ret = ++frog;
*ret = (Edge){s,t,s->first,NULL,cap,0,cost};
return ret;
}
int N,M,S,T;
inline void add(int u,int v,int cap,int cost){
node[u].first = New(&node[u],&node[v],cap,cost);
node[v].first = New(&node[v],&node[u],0,-cost);
node[u].first->rev = node[v].first;
node[v].first->rev = node[u].first;
}
bool spfa(Node s,Node t){
FOR(i,0,N){
node[i].dist = INT_MAX;
node[i].inq = false;
node[i].pre = NULL;
}
std::queue<Node *> q;
q.push(s);s->inq = true;s->dist = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
Node *v = q.front();q.pop();
v->inq = false;
for(Edge *e = v->first;e;e = e->next){
if(e->flow < e->cap && e->t->dist > v->dist + e->cost){
e->t->dist = v->dist + e->cost;
e->t->pre = e;
if(!e->t->inq){
q.push(e->t);e->t->inq = true;
}
}
}
}
return t->pre != NULL;
}
inline int mincost(){
int ret = 0;
while(spfa(&node[S],&node[T])){
int flow = INT_MAX;
for(Node *v = &node[T];v != &node[S];v = v->pre->s){
flow = std::min(flow,v->pre->cap-v->pre->flow);
}
for(Node *v = &node[T];v != &node[S];v = v->pre->s){
v->pre->flow += flow;
v->pre->rev->flow -= flow;
ret += v->pre->cost*flow;
}
}
return ret;
}
int a[MAXN],b[MAXN];
int hMAXN;
int n,m;
int work(int flag){
CLR(node,0);CLR(pool,0);frog = pool;
S = 0,T = n+m+1;
N = n+m+1;
FOR(i,1,n) add(S,i,a[i],0);
FOR(i,1,m) add(n+i,T,b[i],0);
FOR(i,1,n){
FOR(j,1,m){
add(i,n+j,INT_MAX,hi*flag);
}
}
return mincost()*flag;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
FOR(i,1,n) scanf("%d",a+i);
FOR(i,1,m) scanf("%d",b+i);
FOR(i,1,n) FOR(j,1,m) scanf("%d",&hi);
printf("%dn",work(1));
printf("%dn",work(-1));
return 0;
}
<h2>蒜头君的理发店</h2>

这一题直接看不是很好想,我们不如考虑每一个理发师对答案的贡献。
考虑一个理发师接待了 $m$ 位顾客,编号从 $1$ 到 $m$,给第 $i$ 个顾客理发需要花费 $w_i$ 的时间,那么选定一种排列方式 $p$,则该排列方式对应的答案就是 $ \sum_{i=1}^n w_{p_i} * (n-i+1) $。
那么对于每一个理发师我们可以看做是 $m$ 个状态表示,可以拆点第 $i$ 个点表示正在理倒数第 $i$ 个顾客,如果指向顾客 $j$ 表示这个顾客被这个理发师当做了倒数第 $i$ 个顾客(仅对于该理发师独立而言)。
这样建图方法就出来了:我们建立超级源点 $S$ 连向每一个理发师的每一个状态,流量为 $1$ ,费用为 $0$。每个顾客连向超级汇点 $T$ 一条流量为 $1$ 费用为 $0$ 的边。理发师 $i$ 的第 $k$ 个状态连向顾客 $j$ 一条流量为 $1$ 费用为 $k \times t_{i,j}$ 的弧。
跑一边最小费用最大流就可以求得最小总花费,进而求得最小平均花费。
<h3>代码</h3>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define Re register
#define LL long long
#define U unsigned
#define FOR(i,a,b) for(Re int i = a;i <= b;++i)
#define ROF(i,a,b) for(Re int i = a;i >= b;--i)
#define SFOR(i,a,b,c) for(Re int i = a;i <= b;i+=c)
#define SROF(i,a,b,c) for(Re int i = a;i >= b;i-=c)
#define CLR(i,a) memset(i,a,sizeof(i))
#define BR printf("--------------------n")
#define DEBUG(x) std::cerr << #x << '=' << x << std::endl
const int MAXN = 1000+5;
const int MAXM = 1000000+5;
struct Node{
struct Edge first,pre;
int dist;bool inq;
}node[MAXN];
struct Edge{
Node s,t;
Edge next,rev;
int flow,cap,cost;
}pool[MAXM<<1],*frog = pool;
Edge New(Node s,Node *t,int cap,int cost){
Edge *ret = ++frog;
*ret = (Edge){s,t,s->first,NULL,0,cap,cost};
return ret;
}
inline void add(int u,int v,int cap,int cost){
node[u].first = New(&node[u],&node[v],cap,cost);
node[v].first = New(&node[v],&node[u],0,-cost);
node[u].first->rev = node[v].first;
node[v].first->rev = node[u].first;
}
int N,S,T;
inline bool spfa(Node s,Node t){
FOR(i,0,N){
node[i].dist = INT_MAX;
node[i].inq = false;
node[i].pre = NULL;
}
std::queue<Node *> q;
q.push(s);s->dist = 0;s->inq = true;
while(!q.empty()){
Node *v = q.front();q.pop();
v->inq = false;
for(Edge *e = v->first;e;e = e->next){
//DEBUG(e->t->dist);DEBUG(v->dist);DEBUG(e->cost);
if(e->flow < e->cap && e->t->dist > v->dist + e->cost){
e->t->dist = v->dist + e->cost;
e->t->pre = e;
if(!e->t->inq){
e->t->inq = true;
q.push(e->t);
}
}
}
}
return t->pre != NULL;
}
inline int mincost(){
int ret=0;
while(spfa(&node[S],&node[T])){
int flow = INT_MAX;
for(Node *v = &node[T];v != &node[S];v = v->pre->s){
flow = std::min(flow,v->pre->cap - v->pre->flow);
}
for(Node *v = &node[T];v != &node[S];v = v->pre->s){
v->pre->flow += flow;
v->pre->rev->flow -= flow;
ret += flow*v->pre->cost;
}
}
return ret;
}
int n,m;
int tMAXN;
inline int getp(int x,int y){
return (x-1)*m+y;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
FOR(i,1,m) FOR(j,1,n) scanf("%d",&ti);
FOR(i,1,n){
FOR(j,1,m){
FOR(k,1,m){
add(getp(i,j),getp(n,m)+k,1,tk*j);
}
}
}
S = 0;T = getp(n,m)+m+1;
N = T;
FOR(i,1,getp(n,m)) add(S,i,1,0);
FOR(i,1,m) add(getp(n,m)+i,T,1,0);
printf("%.2fn",1.0*mincost() / m);
return 0;
}
<h2>环游世界</h2>

题目显然可以转化为两个人,限制不能有一条边被走了两次,都到达终点的总距离最小的方案。
然后可以转换为求流量为 $2$ 时最小的费用流。
对于原图的双向边在新图中插入一条双向弧,容量为 $1$,费用为边上的距离,源点连向起点一条费用为 $0$ ,容量为 $2$ 的弧,终点连向汇点一条费用为 $0$,容量为 $2$ 的边。
考虑如何处理“容量为 $2$” 这个限制,发现这个图的特殊性质保证每次增广最多能使流量加一,所以最多增广两次即可。

2 comments
orz %%%吴雨航
orz %%%吴雨航